Table of Contents
Dual Coding Theory
General
Dual coding is a theory of cognition introduced by Allan Paivio in late 1960s. This theory suggests that there are two distinct subsystems contributing to cognition: one is specialized for language and verbal information, and the other for images and non-verbal information. According to Paivio,
- “Human cognition is unique in that it has become specialized for dealing simultaneously with language and with nonverbal objects and events.”1)
What is dual coding theory?
- “The most general assumption in dual coding theory is that there are two classes of phenomena handled cognitively by separate subsystems, one specialized for the representation and processing of information concerning nonverbal objects and events, the other specialized for dealing with language.”2)
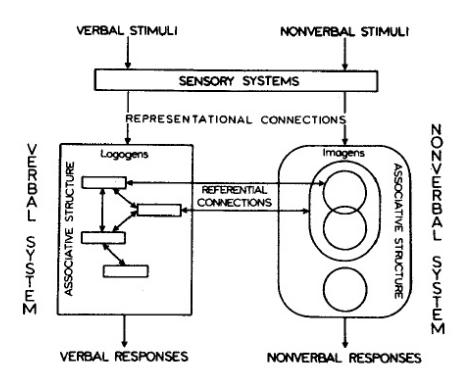
The two mentioned kinds of processing systems, verbal and non-verbal are functionally and structurally independent. This means that each of them can work independently of the other one and that they work on different kinds of representational units. Representational units are “relatively stable long-term information corresponding to perceptually identifiable objects and activities, both verbal and nonverbal.”.3) They are divided into:
- logogens, referring to verbal entities (spoken or written words) and organized in terms of associations and hierarchies, and
- imagens, referring to mental images and non-verbal entities and organized in terms of part-whole relationships.
For example, a written or spoken word will be processed using the verbal processor and stored as a verbal representation - logogen, but a sound not related to language will be processed by the non-verbal processor and stored as a non-verbal representation - imagen. Logogens and imagens are connected with two kinds of connections:
- Referential connections, which represent links between logogens and imagens. Referential connections enable performing operations like imaging to words and namings to pictures or images to words. For example, associations of an image of a school building or an unpleasant feeling (both non-verbal entities) elicited by the word school (a verbal entity).
- Associative connections, which represent connections between logogens or between imagens. Associative connections on the other hand enable forming verbal-verbal or non-verbal-non-verbal associations. For example, the word school can elicit verbal entities blackboard, or boredom.
Both referential and associative types of connections help forming the complex networks of human memory.
Paivio also refers to the issue of problem-solving. Problem-solving is, according to Pavio, the result of joined work of both verbal and non-verbal processing, but if the task is more concrete and non-verbal, the contribution of non-verbal processing system will be more crucial to the outcome and vice-versa.
What is the practical meaning of dual coding theory?
Dual coding theory suggests that combining verbal and graphical material in learning (or just encouraging students to generate appropriate mental images) should increase the probability that words will activate corresponding images and vice-versa.
This also means that learning material will be easier to relate if it is less abstract.
- “… concrete nouns are superior to abstract nouns in their capacity to elicit sensory images, and that imagery can mediate the formation of an associative connection between members of a pair.”4)
Paivio also addresses individual differences in tendency and capacity to use imagery:
- “Students who have trouble imaging , for example, may fail to remember passages of text that benefit from imaginal processing, may not understand geography or other spatial facts in a concrete way, and might do poorly at visualizing the steps in a geometric proof, spelling difficult words or even printing letters correctly.”
Criticisms
Common criticisms of dual coding theory suggest that there is no need for two representational systems, since both verbal and non-verbal stimuli are processed in working memory, turned to semantic elements or propositions and are stored in long-term memory. This assumption is sometimes also known as the single-coding theory.5)
Keywords and most important names
- Dual coding theory, verbal and non-verbal system, logogen, imagen, referential connections, associative connections
Bibliography
Paivio, Allan. Mental Representations: A Dual Coding Approach. Oxford University Press, 1990.
Ryu, Jiyeon, Tingling Lai, Susan Colaric, Joanne Cawley, and Habibe Aldag. Dual Coding Theory. 2000.
Read more
Paivio, Allan. Imagery and verbal processes. Holt, Rinehart and Winston. New York, 1971.